![[Loiret]](../images/v/vxt-d4750.gif)
![[US Dept of State]](../images/v/vxt-d4751.gif)
Flag of Loiret, France (fotw);
Department of State, US (fotw)
![[Bermuda]](../images/v/vxt-d2130.gif)
![[St. Maarten]](../images/v/vxt-d2129.gif)
![[American Samoa]](../images/v/vxt-d2131.gif)
Flag of Bermuda (fotw); Flag of St Maarten (fotw); Flag of
American Samoa (fotw).
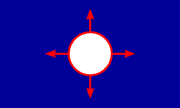
Flag of the Union of British Columbia Indian Chiefs, Canada (fotw)



Flag of the Free Aceh Movement, Indonesia (fotw);
Flag of the Alsace-Lorraine Separatist movement, France (fotw);
Flag of the South Sudan Independence Movement (fotw)
2) See ‘Union flag’.

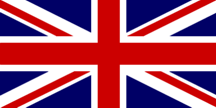
Union Flag 1606 – 1801, England/UK (fotw); Union Flag, UK (fotw)
![[Flag of Celebration]](../images/v/vxt-d3619.gif)
Flag of the Mardi Gras Celebrations, Mobile, US (fotw)
![[Flag of Ceremony]](../images/v/vxt-d3161.gif)
Flag of Ceremony/Indoor Flag of the Secretary of Agriculture, US (fotw)
Please note that this term is a direct translation of the Spanish "Bandera de Ceremonia" and should not be confused with a ceremonial ensign/or flag as listed separately herein.
![[flag of command]](../images/v/vxt-d3784.gif)
![[flag of command]](../images/v/vxt-d3785.gif)
![[flag of command]](../images/v/vxt-d3786.gif)
Flags of an
Admiral, Vice
Admiral and Rear Admiral,
USN (fotw)
Notes
1) Although these terms are sometimes
considered interchangeable, the Editors have drawn a general distinction between
the command flags used by senior naval officers, the rank flags employed by officers
from the other armed services, the distinguishing flags of civilians and with
personal flags.
2) A further distinction has been drawn between
the flag of command which replaces the masthead pennant, and command pennants
which do not.
![[flags of convenience]](../images/v/vxt-d2041.gif)
![[flags of convenience]](../images/v/vxt-d2879.gif)
![[flags of convenience]](../images/v/vxt-d4235.gif)
National Flags/Civil Ensigns of Panama,
Liberia and
Belize (often flown as a flag of convenience)
Please note that although in widespread use prior to this date, the flag of defiance did not appear in English naval Instructions until 1647 (and was dropped in 1799) – see ‘red flag 2)’ and its following note.
![[flags of distress]](../images/v/vxt-d149.gif)
![[flags of distress]](../images/v/vxt-d3390.gif)
![[flags of distress]](../images/v/vxt-d3391.gif)
![[flags of distress]](../images/v/vxt-d3392.gif)
Signal Flag Victor (fotw);
Signal Flags November–Charlie (fotw);
Coast Guard Signal US (official website)
Notes
a) While some may still acknowledge
an upside-down ensign as a signal of distress, it is no longer recognized under
international rules; and that the waft, also previously used, is now entirely
obsolete (see also
‘International Code of Signal Flags’,
‘signal flag’ and
‘waft’).
b) According to the US Coast
Guard regulations the orange flag should be either square with vertically arranged
symbols, or rectangular with the square and disc horizontal, and that
a very similar signal is recommended in the ICS for identification from the air (see also
‘International Code of Signals’).
![[Austro-Hungary flag of honor]](../images/v/vxt-d504a.gif)
![[Austro-Hungary flag of honor]](../images/v/vxt-d504.gif)
Austro-Hungary 1850 – 1918 (fotw)
Please note that the term honour flag has been used for two other designs issued by different authorities under differing circumstances, and it is therefore suggested that this form of the term should be applied only to those flags – see ‘honour flag 1)’ and ‘honour flag 2)’.
![[flag of pretence]](../images/v/vxt-d1482.gif)
![[flag of pretence]](../images/v/vxt-d3304.gif)
![[flag of pretence]](../images/v/vxt-d1484.gif)
National Flag of Comoros (fotw); Naval Ensign of
Bolivia (fotw); 51 Star Flag of The United States (fotw)
Notes
a) The 51 star flag of the United states displays one more star
than there are states in the Union, whilst the national flag of Comoros or the naval
ensign of Bolivia for example (and illustrated above), show one more star than they
have provinces under their current control.
b) An “anticipatory flag”, on the other hand,
such as a 39 star flag of the United States, displays a symbol of granted statehood but
in advance of its official appearance on the flag.
Please note regarding 2) that the “protectorate” in question retained control over its internal affairs, but that their foreign policy was entirely handled by the relevant protecting power.![[flag of protection]](../images/v/vxt-d3578.gif)
![[flag of protection]](../images/v/vxt-d4122.gif)
Flag of the Red Cross (fotw); Naval Ensign,
UK (fotw)
![[flag of St. George]](../images/v/vxt-d001.gif)
Command Flag of a Full Admiral, UK (fotw)
![[air force flag]](../images/v/vxt-d2538.gif)
![[air force flag]](../images/v/vxt-d2539.gif)
![[air force flag]](../images/v/vxt-d4123.gif)
Flag of the Air Force, Peru (fotw); Flag of the
Air Force, Portugal (fotw); Ensign of the
Air Force, Ghana (fotw)
![[flag of the army]](../images/v/vxt-d2541.gif)
![[flag of the army]](../images/v/vxt-d2542.gif)
![[flag of the army]](../images/v/vxt-d2740.gif)
Flag of the
Army, UK (fotw); Flag of the
Army, China (fotw);
Flag of the Army, South Africa (fotw)
![[Marine Corps flag]](../images/v/vxt-d202.gif)
![[Marine Corps flag]](../images/v/vxt-d204.gif)
![[Marine Corps flag]](../images/v/vxt-d2741.gif)
Flag of the Marine Corps, US (fotw); Flag of the
Marine Corps, Brazil (fotw); Flag of the
Marine Corps, Taiwan (fotw)
![[flag of navy]](../images/v/vxt-d2543.gif)
![[flag of navy]](../images/v/vxt-d2742.gif)
![[flag of navy]](../images/v/vxt-d2544.gif)
Flag of the Navy, US (fotw);
Flag of the Navy, Colombia (fotw);
Flag of the Navy, Peru (fotw)
![[flag of the state of Arkansas]](../images/v/vxt-d4363.gif)
![[flag of the state of Arizona]](../images/v/vxt-d3305.gif)
![[flag of the state of Arkansas]](../images/v/vxt-d4364.gif)
Flags of the States of Arkansas and
Arizona,
US (fotw); Flag of the State of
Tachira, Venezuela (fotw)
![[Flag of tolerance]](../images/v/vxt-d1485.gif)
Flag Representing the Balance of Life (fotw)
![[Flag officer flag]](../images/v/vxt-d4124.gif)
![[Flag officer flag]](../images/v/vxt-d4126.gif)
![[Flag officer flag]](../images/v/vxt-d4127.gif)
Rank Flags of an Admiral, Vice Admiral and Rear Admiral,
France (fotw)
Please note with regard to 2) that in Royal Navy usage all admirals were formerly considered to be flag officers, but that the term is now restricted to those of that rank who are entitled to fly a flag of command aboard ship.
![[flag officer's broad pennant]](../images/v/vxt-d1230.gif)
Yacht Club
Vice-Commodore’s Broad Pennant, Finland (fotw)



National Arms Ecuador (fotw);
Naval Ensign and National
Arms, Colombia (fotw)
Notes
a) Three further examples would be the pre-1994 National Flag of South Africa,
the National Flag of Haiti and the National Arms on the War Flag of Peru.
b) This category does not include those flags
or ensigns whose canton consists of another flag (such as the British or Indian red
ensigns) and for which the term canton flags should be used (see
‘canton flag’).

![[flags of defiance]](../images/v/vxt-d990.gif)
![[Flag of truce]](../images/v/vxt-d1170.gif)
![[Flag of war]](../images/v/vxt-d347a.gif)